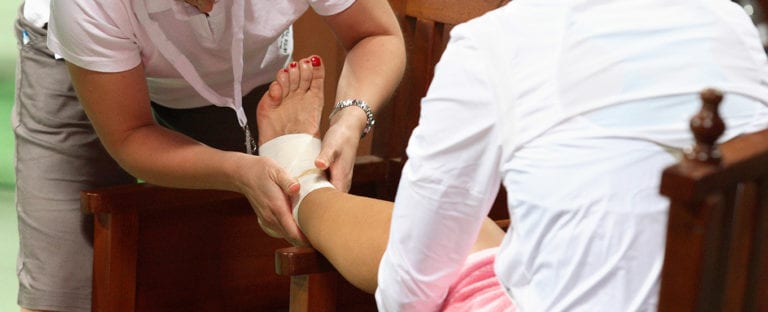
Seeing as an estimated 25,000 ankle sprains occur per day in the United States, it’s no surprise that thousands of people each day are looking for ways to remedy their newly injured ankle. As an athletic trainer who has diagnosed and treated thousands of ankle injuries over the past thirty years, here is my step-by-step guide for what you should do when you sprain your ankle.
Diagnosing an Ankle Injury
It’s important to take a close look at your ankle immediately after the injury occurs since swelling and pain can make injury evaluation difficult several hours later when the joint is starting to get stiff and sore. Generally speaking, there are two types of ankle sprains that are diagnosed depending on where the injury is located on the ankle – the low ankle sprain and the high ankle sprain. In this post we are going to mainly discuss the low ankle sprain, but you can read more info on high ankle sprains here.
For the classic inversion ankle sprain the main site of pain and usually swelling is localized on the lateral/outside of the ankle. Alternatively, if you have suffered an eversion ankle sprain, the pain and swelling with occur mainly on the inside of the ankle.
Discomfort and pain is usually evident when the injured person tries to walk. Discoloration of the skin can occur from 24 to 48 hours after the injury, starting on the lateral side of the ankle then spreading with gravity.
If after 24 hours your pain is mild, you have little swelling and can walk on your ankle with little or no pain, it’s probably just a mild Grade 1 ankle sprain. If you have any severe pain or swelling you should consult with a medical professional as it’s possible you may have a Grade 2 or Grade 3 ankle sprain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the items below it’s best to consult a medical professional:
- If anything looks abnormal when compared to the opposite leg and ankle.
- If you heard a popping sound when the injury occurred which may indicate a torn ligament or fracture.
- If you can’t walk due to pain, or your ankle feels unstable when you stand.
- If your injury shows no improvement after 3-4 days
Do you Have Access to a Certified Athletic Trainer?
If you are playing on a high school or collegiate team your school probably employs an athletic trainer. Even if you are playing on a club team you still probably know an athletic trainer that works at your school that could help you out. Athletic trainers have extensive knowledge in evaluating ankle injuries and can provide both treatment and rehabilitation protocols to get you back on your feet and return to activity.
Recovering from an Ankle Sprain
After one ankle injury, you are 70% more likely to sustain another ankle injury. The ankle joint is supported by ligaments and once these ligaments are stretched/torn due to an ankle sprain, they remain stretched. This causes the joint to become loose and unstable making yet another ankle injury much easier to obtain. In order to stop this mechanism of injury and help to prevent future ankle injuries, the proper steps must be taken to recover from an ankle sprain.
- Seek Medical Attention if Needed – Failure to properly identify all possible damage to your ankle may lengthen healing time and cause more damage.
- Move Early – Perform some gentle range of motion exercises right after injury help to improve functional outcomes and may decrease your return-to-play time.
- Protect and Support – Wear the appropriate ankle brace support system until your injury has healed and you can evaluate your next steps.
- Control Pain – Use the RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) method to help control pain in addition to anything recommended by your medical professional.
- Strengthen – Perform any physical therapy exercises specifically prescribed to you as you recover from your injury.
- Help Prevent Future Ankle Injuries – Even with strong muscles, perfect biomechanics, and great conditioning, ankle sprains are still possible and in some situations highly likely to occur. After spraining your ankle, the best way to prevent reoccurring ankle injuries and further damage to your ligaments is to wear a preventative ankle brace that is comfortable to wear and provides full range of motion. Lace-up ankle braces are not recommended due to their negative impact on strength and performance/range of motion.
When it comes to ankle sprains and injuries, every situation is different. The notes above should serve as a guide to helping you after you sprain your ankle but do not take the place of medical advice. Should you have any questions about specific ankle injuries or ankle braces please reach out to our certified athletic trainers or leave us a message in the comments below.
SHARE WITH FRIENDS
RECENT POSTS
POST BY TOPIC
- Acute Ankle Injuries (7)
- Ankle Bracing (33)
- Ankle Injuries (17)
- Ankle Injury Prevention (19)
- Ankle Instability (4)
- Athletic Trainers (2)
- Athletic Training (3)
- Basketball (6)
- Football (9)
- Hiking (2)
- injury (2)
- Mild/Moderate Ankle Injury (2)
- News (2)
- Osteoarthritis (5)
- Pickleball (3)
- Soccer (4)
- Sports (17)
- Tennis (3)
- Ultra 360 Lace-Up (2)
- Ultra CTS (6)
- Ultra Zoom (9)
- Uncategorized (2)
- Volleyball (8)